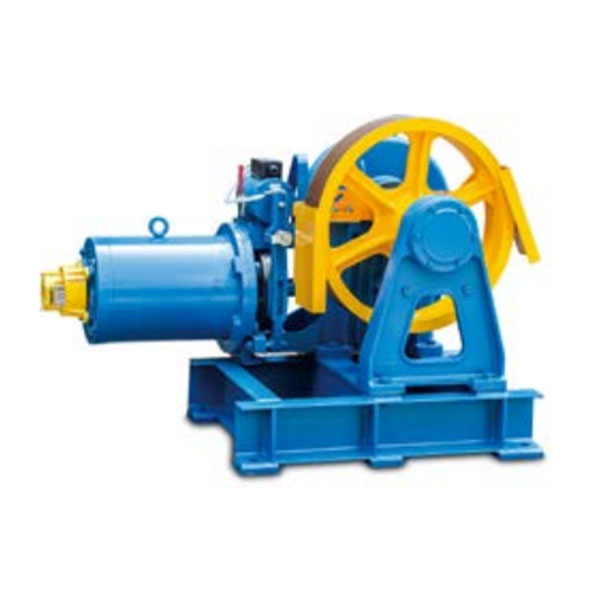
Asynchrone oandreaune lifttraktaasjemasine THY-TM-YJ200A
| Suspension | 1:1 |
| Maks. statyske lading | 6000 kg |
| Kontrôle | VVVF |
| DZE-9EA Rem | DC110V 1.5A |
| Gewicht | 580 kg |
1. Snelle levering
2. De transaksje is mar it begjin, de tsjinst einiget nea
3.Type: Traksjemasine THY-TM-YJ200A
4. Wy kinne syngroane en asynchrone traksjemasines leverje fan TORINDRIVE, MONADRIVE, MONTANARI, FAXI, SYLG en oare merken.
5. Fertrouwen is lok! Ik sil dyn fertrouwen noait teloarstelle!
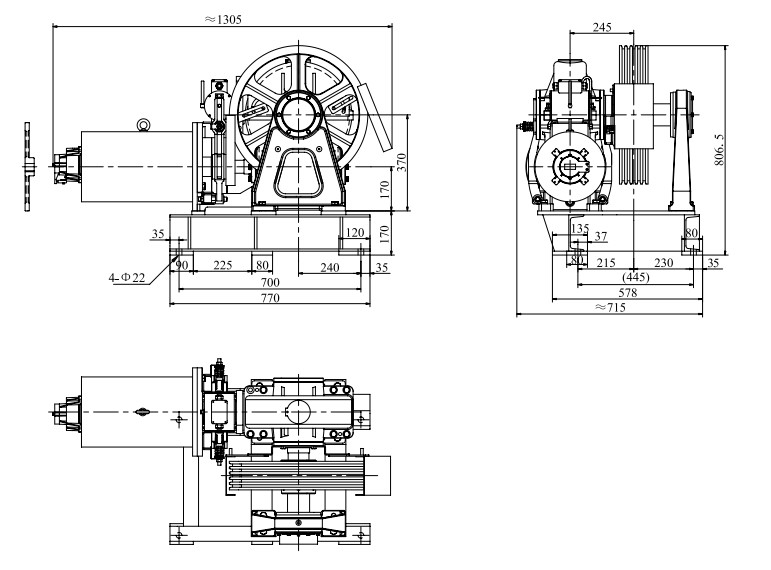
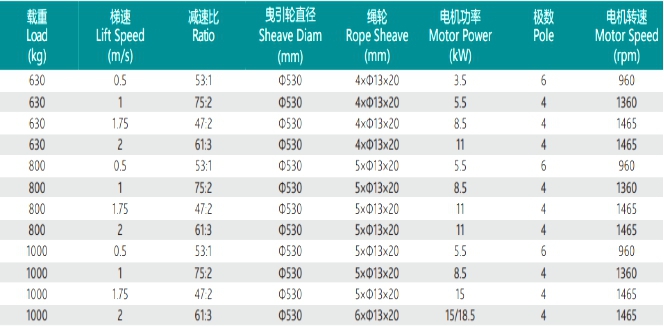
De THY-TM-YJ200A asynchrone lifttraktormasine mei fersnellingsbak foldocht oan de relevante regeljouwing fan 'e noarmen TSG T7007-2016, GB 7588-2003, EN 81-20:2014, EN 81-50:2014. It remmodel dat oerienkomt mei de traktormasine is DZE-9EA. It is geskikt foar frachtliften mei in laadkapasiteit fan 630KG ~ 1000KG. It brûkt in wjirmtandwielreduksjetype. It wjirmmateriaal is 40Cr en it wjirmwielmateriaal is ZQSn12-2. De masine is rjochtsmonteare en loftsmonteare is beskikber. De YJ200A traktormasine wurdt levere mei in traktormasineframe, standert foarsjoen fan in hânwiel foar in trommel, motorfermogen ≥ 15KW, de diameter fan it trommelwiel is Φ500, en de rest is Φ320. Neffens ferskate nasjonale noarmen en gebrûksomjouwing kin de masine konfigurearre wurde mei UCMP as nedich.
1. Foldogge oan de nasjonale standert, Jeropeeske standert en Amerikaanske standert, universeel jildend;
2. Twa-wei funksje, realisearje UCMP en overspeed beskerming tagelyk;
3. In set ûnôfhinklike remkomponinten is feiliger;
4. Adoptearje traksjewielremtype;
5. De wriuwingplaat hat in lange libbensdoer;
6. It kontrôlesirkwy wurdt loskeppele om de aksje te triggerjen, en de rêding kin mei de hân iepene wurde yn gefal fan stroomûnderbrekking;
7. Resette ûnderhâldsoperaasje nei efterút nei meganyske aksje;
8. Koarte remreaksjetiid;
9. Yntegreare ûntwerp, gjin ynstallaasje op lokaasje is fereaske. Dit ûnderdiel wurdt ûnder de traksjeskyf ynstalleare om ynterferinsje te foarkommen.
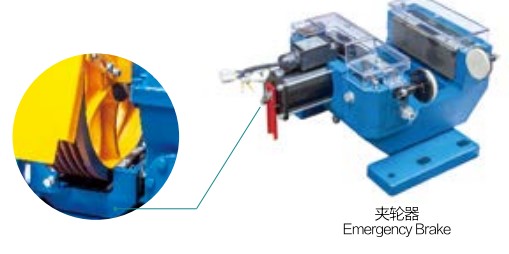
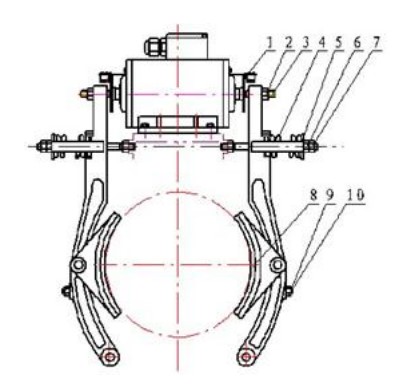
1. Ynstelling fan remkrêft: Draai moer 6 en moer 7 oan it haadfearein los om de fear yn in frije steat te bringen, lûk oan de moer 6 om de fearkap 5 ticht by it frije ein fan 'e fear te bringen, ûntfang in lichte krêft, en draai de moer mei de klok mei 6 Om genôch remkrêft te krijen, draai dan oan mei moer 7;
2. Oanpassing fan 'e remskuon: it remsysteem is yn 'e steat fan hâldrem. As de drukfear genôch druk genereart om de remarm te komprimearjen, is it bôge-oerflak fan 'e remskuon tichtby it bôge-oerflak fan it remwiel. Op dit stuit wurdt it ûnderste ein fan 'e remskuon oanpast. 9 fan 'e skroef sadat de skroef krekt oan it ûnderste ein fan 'e remskuon sit. As de rem aktivearre wurdt om de rem los te meitsjen, draai dan de skroef 9 tsjin de klok yn, en brûk in voelermaat om de gat tusken de remskuon en de twa bôge-oerflakken fan it remwiel te mjitten. As de gat oanpast is om yn prinsipe gelyk te wêzen boppe en ûnder, brûk dan de moer 10 om de skroef oan te draaien.
3. Oanpassing fan 'e iepening fan 'e rem: meitsje moer 2 los, aktivearje de rem, mjit de iepening tusken de remskuon 8 en de twa bôge-oerflakken fan it remwiel mei in voelermaat nei it iepenjen fan 'e rem, en soargje derfoar dat de iepening tusken de remskuon en de twa bôge-oerflakken fan it remwiel 0,1-0,2 mm is (yn prinsipe is it oan te rieden om te soargjen dat der gjin wriuwing is tusken de remskuon en it remwiel by it iepenjen fan 'e rem). As de iepening te lyts is, moat de skroef 3 mei de klok mei draaid wurde om de iepening tusken de skroef 3 en de sluterkap te ferminderjen, en oarsom om de iepening te fergrutsjen. As it ynsteld is yn in juste posysje, brûk dan moer 2 om skroef 3 goed fêst te setten. Kontrolearje opnij oft de leechdraaiende slag fan 'e rem oan 'e easken foldocht.
4. Oanpassing fan syngronisaasje fan it iepenjen fan 'e rem: set de remkrêft oan en út en observearje de snelheidssynchronisaasje fan 'e remarm by it iepenjen fan 'e rem. As de iene kant rapper is en de oare kant stadich, en it remkoppel genôch is, sil it stadigere ein de remaksje koarter meitsje (de skroef losmeitsje), krekt oarsom, it rapper ein fergruttet de remslach (draai de skroef oan). Pas oan wylst jo observearje, en draai de moer fêst oant it syngronisearre is. Kontrolearje opnij oft de idle-slach fan 'e rem oan 'e easken foldocht.
Nei de oanpassing, kontrolearje oft de ûnderdielen mei ûnderling ferbûne fergrendelingsrelaasje fêst sitte, en fier in remkrêfttest of statyske ladingstest fan 'e lift út. As it eksperimint mislearret, moat de lift opnij oanpast wurde. As de remkrêfttest net kwalifisearre is, is it strang ferbean om de lift mei elektrisiteit te brûken, oars kin in persoanlik ûngelok foarkomme.